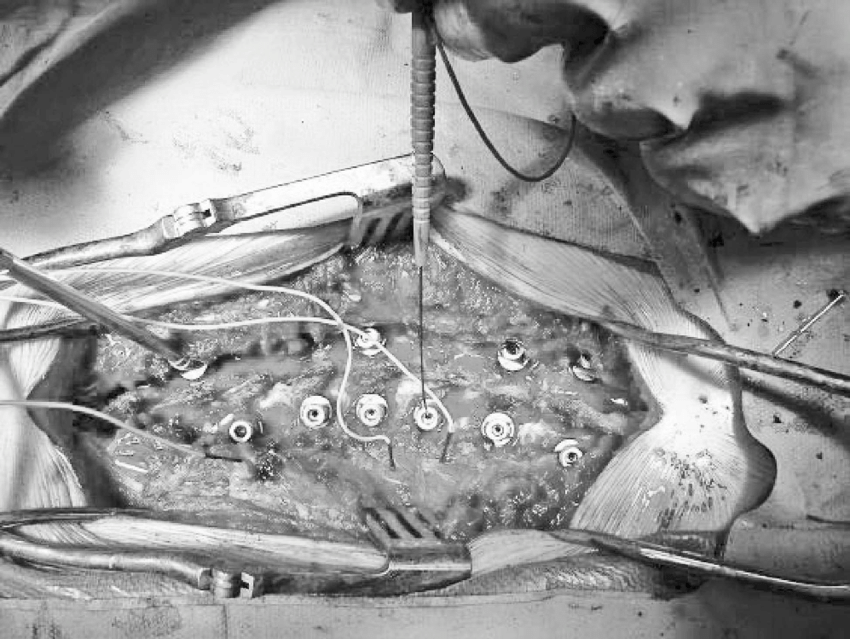
Introduction of Triggered Electromyography.
- Triggered electromyography (EMG) is a technique used to assess the electrical activity of muscles in response to specific stimuli. It involves delivering a stimulus, such as a electrical pulse, and then measuring the resulting muscle activity through EMG electrodes.
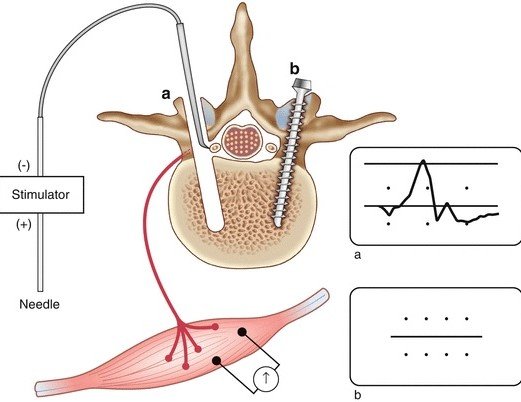
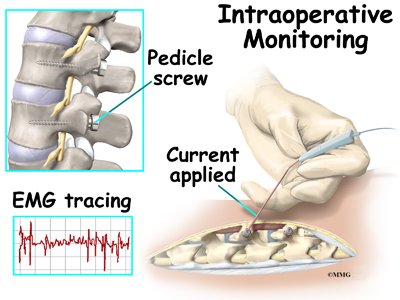
picture of monopolar pedicle probe to stimulate the trajectory before placing the pedicle screw.

Intensity of Stimulus for Triggered Electromyography.
- For electrical stimuli the intensity is usually we measured in milliamperes (mA) or volts (V). The intensity should be set at a level that threshold or reliably triggers a response without causing nerve injury due to high intensity of current to the patient
Pulse /Stimulus Duration.
- The duration of the stimulus pulse or signal is another important parameter. It can be measured in or microseconds (μs) or milliseconds (ms) . The duration should be sufficient to elicit a measurable response but not excessively long to avoid thermal injury or fatigue effects. to avoid cell fatigue should be maintained inter stimulus interval ISI.
Criteria of triggered .
- The criteria term used to define a “triggered” response can vary. For example, in auditory trigger EMG, the response may be based on the amplitude and latency of the muscle response following the auditory stimulus, auditory stimulus also helps surgeon in real time to preserve/safe the functional tissue .
How to record and Parameters:
- Once triggered, the EMG signal is recorded using electrodes placed on or near the target muscle. Parameters such as sampling rate (measured in Hz or kHz), filter settings {e.g, bandpass filters to isolate EMG signals}, to avoid unnecessary signal can interfere with the true signals, for example 50to 60Hz electrical artifact .Note { Now a days in every intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring IONM machine available switch on this technic to avoid breach of signals}
Conclusion
- It is a important to know while doing triggered electromyography TEMG in cranium and spine cases current should be enough to heat the targeted tissue, to get/receive the Compound Muscle Action Potentials {CMAPs} , from here false positive / false negative can be prevented .
- Current shunting is a also problem to avoid this problems while stimulating any tissue at surgical site , field should be clear like water irrigation , cautery ,patty , blood clot etc these type of thing should remembered .
Related to this article in different area.
https://neurointraoperative.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=1727&action=edit
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1878875021005623
Question.
- What is the meaning of Triggered EMG?
- What parameters has to apply?
- How much intensity of current is required to elicit the muscle potentials?.
- Which type of cases we can prefer this modality?.
- Trigger EMG major role?

1 thought on “Triggered Electromyography.”