Brief about Triggered Electromyography.
Triggered electromyography {TEMG} is a modality used to evaluate the integrity and function of specific muscles by stimulating a motor peripheral nerve and recording the resulting muscle response. Triggered EMG provides valuable information about the nerve and muscle {neuromuscular system}.
Stimulation Parameters.
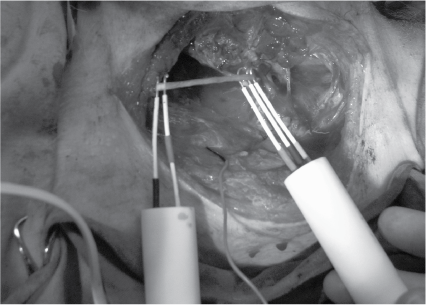
- Stimulation Site. The motor nerve innervating the target muscle is stimulated using a monopolar ,bipolar and concentric bipolar hand held nerve stimulator. Common sites for stimulation include peripheral nerves such as the facial nerve, lower cranial nerve, or oculomotor nerve.
- Type of Stimulation. Electrical stimulation is most commonly we use in our routine IONM cases for triggering EMG responses. The stimulation intensity is set at a level that is sufficient to depolarize nerve fibers and evoke a muscle response.
- Frequency of Stimulation. A single pulse or repetitive stimulation can be used to elicit muscle contractions and record the corresponding EMG responses.
- Stimulation Amplitude. The stimulation intensity should be adjusted to obtain a consistent and measurable muscle response, typically ranging from submotor threshold to supramotor threshold levels.
- Stimulation.
- Cathode hand held probe.
- Wave form. square wave, single pulse.
- Duration stimuli. 200-300 microseconds.
- Frequency: 1.0–4.0 Hz.
- Intensity: 2-5 mA for screening, then decrease the intensity to detect threshold.
Parameters for Recording.

- Sites of Recording . EMG electrodes are placed over the target muscle like glossopharyngeal nerve innervated myotome the stylopharyngeus muscle of the pharynx or muscles to record the muscle response following nerve stimulation. The recording electrodes may be inserted into the muscle intramuscular EMG.
- Recording Configuration. Differential recording configurations are commonly used for triggered EMG recordings. Differential recording provides a more focused and selective assessment of muscle activity .
- Amplification and Filtering: EMG signals are amplified and filtered to enhance the signal quality and reduce noise interference. Bandpass filter settings are usually adjusted to isolate the muscle response frequencies of interest like 20Hz-3KHz and amplification 10,000 times to capture rapid changes in muscle activity following nerve stimulation.

- Above parameters can be modified as per clinician or institute for muscle contraction or motor unit recruitment.
Related to this article.
https://neurointraoperative.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=1676&action=edit
Question.
Why TEMG is important?
Muscle relaxant should be used ?.
Why threshold stimulation is essential?.
Isoflurane is useful?

1 thought on “Triggered Electromyography for cranium surgery.”