What We face problems to record Motor Evoked Potentials MEP in spine cases, Even though power is good enough.

This is my experience sharing with all of you and also believe many people facing same problems whoever working in this field , we stuck also in Operation Room {OR} in front of surgeon.
Here we will try to understand why it is happening and what are possibilities .
Motor Pathways.
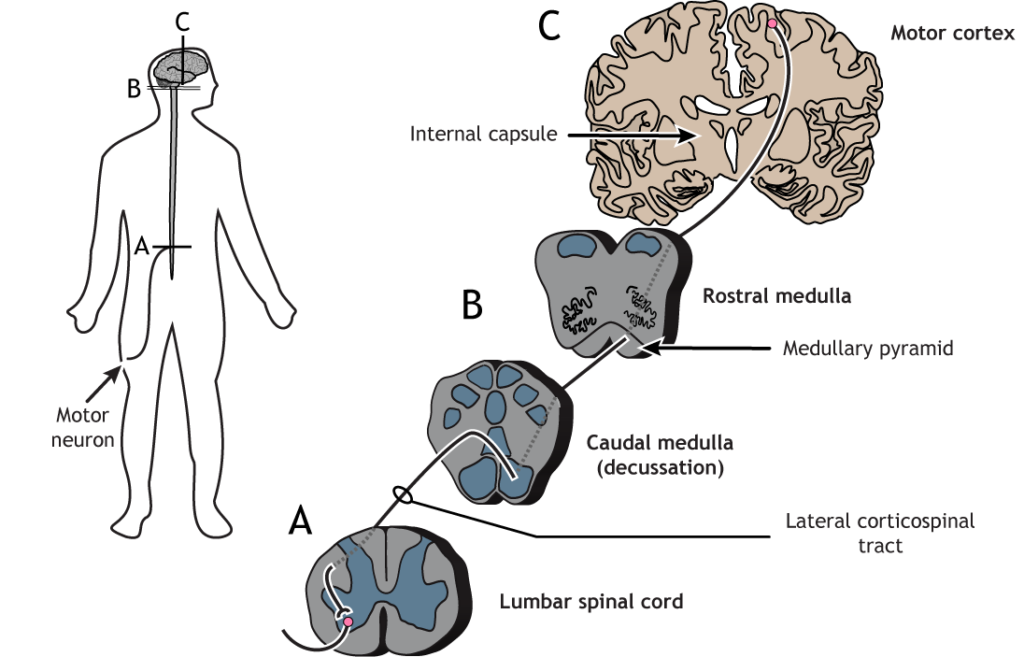
MEPs help monitor the descending motor pathways, which can be divided into two systems.
Lateral System.
Includes the corticospinal tract and a smaller rubrospinal tract. The corticospinal pathway originates mainly in the primary motor cortex (Brodmann’s area 4), with contributions from other regions like the premotor and somatosensory cortices.
Medial System.
Innervates trunk and proximal limb muscles. Fibers from the motor cortices descend bilaterally without crossing the midline.
MEPs are recorded by stimulating the motor cortex (either directly or transcranially) and observing the resulting muscle contractions. These contractions are detected using recording electrodes placed on corresponding muscles.
Brief
- In the context of intraoperative monitoring during surgical procedures, MEPs are commonly used to assess the function of the motor pathways and monitor for potential damage or impairment
- When motor evoked potentials (MEPs) are not recordable in response to a brisk reflex, it may indicate a disruption in the neural pathways involved in motor function. MEPs are neurophysiological responses that are elicited by stimulating the motor pathways and can provide information about the integrity of the central nervous system.
Brisk reflexes, on the other hand, typically refer to hyperactive reflex responses that may be indicative of neurological conditions or abnormalities.
- If MEPs are not recordable in response to a brisk reflex, it may suggest that there is a blockage or interruption in the neural pathways that are normally responsible for transmitting motor signals.
- This can be concerning as it may indicate a potential nerve injury, compression, or dysfunction that is affecting the transmission of motor signals
Poor signals.
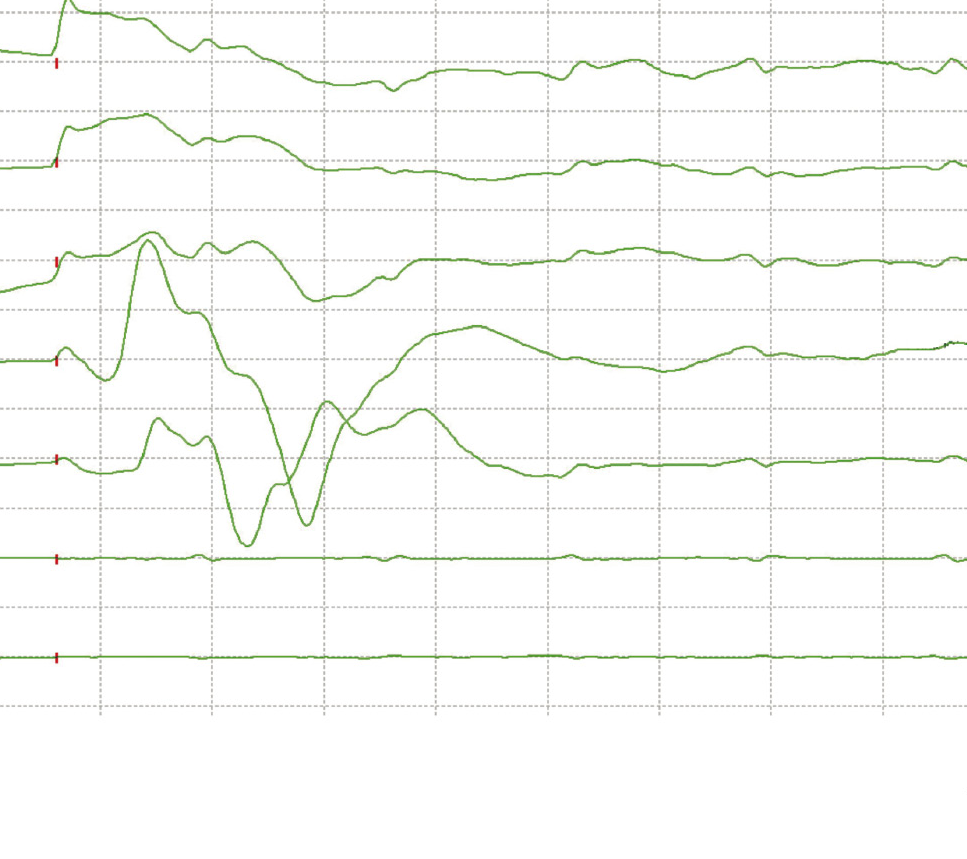
- In such cases, it is important for the healthcare team to closely monitor the patient and investigate the underlying cause of the lack of MEP response.
If motor evoked potentials (MEPs) are not recordable in brisk reflex, it may indicate a possible issue with the transmission of signals along the motor pathways. But also to rule out potential causes for the unrecordability of MEPs in this situation, the following steps can be taken.
Confirm Proper Stimulation Technique.
- Ensure that the stimulation technique used to elicit MEP responses is appropriate. This includes positioning the stimulating corkscrew electrode correctly over the motor cortex and using the correct intensity and frequency of stimuli.
Check for Muscle Relaxation.
- Make sure that the patient is adequately relaxed before performing MEP testing. Brisk reflexes can sometimes interfere with the recording of MEPs due to muscle activity and movement artifacts.
Rule Out Technical Issues.

- Check the equipment for any technical issues that may be affecting the recording of MEPs. This includes ensuring that the electrodes are securely connected, that the amplifiers are functioning properly, and that there is no interference from other electrical equipment.
Monitor Muscle Response.
- In cases where MEPs are not recordable, it is important to monitor the muscle response to other forms of stimulation, such as electrical stimulation of peripheral nerves. This can help determine if the lack of MEP response is due to a central or peripheral issue.
Consider Alternative Testing Methods.
If MEPs are not recordable, other neurophysiological tests can be performed to assess motor function, such as D wave , electromyography (EMG), or somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs). These tests can help localize the site of dysfunction within the motor pathways.
Consult with a Neurologist or Neurophysiologist: If MEPs remain unrecordable despite troubleshooting, it may be necessary to consult with a neurologist or neurophysiologist for further evaluation and management.
conclusion
By systematically ruling out potential causes for unrecordable MEPs in the context of brisk reflex, healthcare professionals can determine the best course of action for further evaluation and management based on the individual patient’s clinical presentation.
{Note- I hope this article may be useful for you because most of the neurophysiology people stuck in Operation room specially when surgeon asks patient is able to walk or supportive walk.}
Related to this article.
https://neurointraoperative.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=1832&action=edit
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7692772
Question.
What is the meaning of brisk reflex?
How much can affect the signals of evoked potentials when reflexes are brisk?.
Why we do not get good baseline in brisk reflexes, even power is good enough ?.
How to check Muscle relaxant affect during surgery?
How to rule out technical glitch?.

Check for Muscle Relaxation.
Make sure that the patient is adequately relaxed before performing MEP testing. Brisk reflexes can sometimes interfere with the recording of MEPs due to muscle activity and movement artifacts.
Should the muscle be adequately relaxed to monitor MEPs, I think you meant not relaxed because muscle relaxation will make you not to get MEPs
Yes correct before stimulate the patient make sure subject should be relax like adequate dose of TIVA drugs because some time we get muscle artifact specially in exaggerated reflex.
But patient should be out of muscle relaxant so TOF another tool available in every IONM machine.