Local Stimulation.
In a term of cauda equina syndrome Like Lipomeningomyelocele, Tethered Cord Syndrome Or spina bifida, if subject/patient presenting with paraparesis in that case local stimulation {Triggered Electromyography TEMG} can be a crucial modality for neuro-surgery.
To Easy Understanding Cauda Equina Syndrome?.
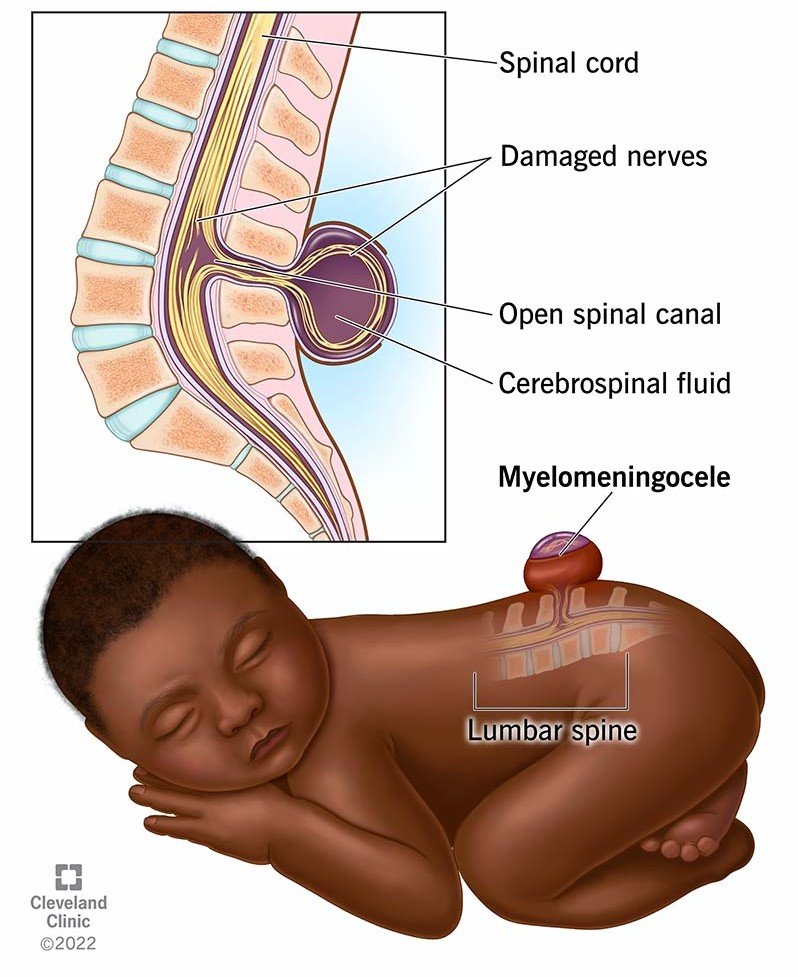
- Brief about CES- Cauda Equina Syndrome usually occurs due to the compression of the nerve roots at the lower end of the spinal cord {where ending cord} (the cauda equina), leading to neurological deficits.
- Sign and Symptoms: These may include lower extremity weakness {paraparesis} partial/transient weakness of lower extremities. motor/sensory loss, bowel and bladder dysfunction.
To Approaches a Local Stimulation .{Functional Electrical Stimulation}.
- Real time Electrical Stimulation {RTES}- It can be used to activate the paralyzed/weak muscles, to see the nerve continuity , as well as it enhance functional mobility.
Purpose.
- Intraoperative Tool– To assess the function of individual nerve roots and their muscles affected by cauda equina syndrome.
What are the Procedure.
- Placement of Electrode- At least 3 centimeter long needle electrodes to access the proper depth of muscle fibers, to be placed over the myotomes innervated by the affected nerve roots. or site of detethering of cord.
- Real time Stimulation– Local electrical stimulation/Triggered electromyography to be applied over the nerve root directly to elicit the muscles responses.{Electromyogram}
Types of probe. Bipolar probe will be preferable in case of direct roots stimulation.
Type A- 3-5 mm millimeter space bipolar probe.

Type B- 1 mm ,millimeter space one Concentric bipolar probe .

- Recording Responses which is being elicited by local stimulation at perioperative period– The electrical activity in the muscles being recorded, using the EMG setup/ Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring IONM machine, allowing assessment of muscle response to stimulation.
Analysis of Findings
- Latency and Amplitude-Changes in latency (time taken for response by stimulation) and amplitude (strength of muscle fibers response) can indicate the nerve function as well as degree of dysfunction.
- Strength of stimulus- Here we have to understand that, the threshold of intensity/current will be higher, because here dealing with affected nerve roots{ paraparesis case} not intact one ,which means threshold of stimulus will be little higher compare what we do in intact neurological condition. {For example- 0.3-0.5 milliampere is good amount of current to facilitate the electromyogram in a intact neurological conditioned but same this threshold will not be applied in a paraparesis case because nerve roots all ready compromised due to anatomical pathology.}
Parameters for local stimulation.
- As slandered TEMG settings like in form of square pulse, single pulse ,pulse duration 300 microsecond at the rate of 3 Hz .
- Start the current from 0.9 -1.5 milliampere and adjust the threshold base on response.
Clinical Applications.
Identifying Nerve Root Involvement: Local stimulation helps pinpoint specific nerve roots that may be compressed or damaged
Monitoring Recovery: Repeated EMG assessments can help monitor the progress of recovery and adjust interventions accordingly.

Using a local stimulation-triggered EMG can provide valuable insights into the functional status of nerves and muscles in cauda equina syndrome.
Related to this article.
https://neurointraoperative.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=1468&action=edit
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24506341
Questions?.
What we understand about Local stimulation?.
How it can help in those cases like paraparesis patient?.
Why still its useful even power is not enough good?.
What is the important role of anesthetist in these type of cases?.
Why importance of IONM ?.
