About TCEMEPs Or SSEPs.
- While monitoring being performed for perioperative neurophysiological monitoring, changes during procedure, both TCEMEPs {Transcranial Electrical Motor Evoked Potentials} and SSEPs {Somatosensory Evoked Potentials} will be important, but the choice of monitoring technique depends on the surgical procedure and the structures at risk.
- As we know the physiology Transcranial Electrical Motor Evoked Potentials assess the real time function of motor pathways {Descending Tract- Direct Pyramidal indirect extrapyramidal fibers}
- Somatosensory Evoked Potentials serves the function of dorsal column medial lemniscus indirect spinothalamic tract {ventrolateral/anterolateral) system} because these fibers ascending along with DCML tract.
Surgeon's Quarries? TCEMEPs Or SSEPs?

- Purpose to write this article because many surgeon, anesthetist and other medical professionals asks which modality to be used in surgery like spinae or cranium cases. Here they have to understand the importance of modalities because each modality covers specific tract, for example motor evoked potentials assess the only function of motor pathway which means during procedure if something goes wrong in corticospinal tract nothing will change in sensory evoked potentials because these are individual tract and also like something goes wrong in posterior tract nothing will change in ventral cord signals. So multi modality techniques are most preferable rather than single, single example -only TCEMEP/SSEP or TEMG.
TCEMEPs {Transcranial Electrical Motor Evoked Potentials}.

- Principle-TCEMEPs monitors the motor pathways, specifically the corticospinal tract, which is crucial for voluntary muscle movement.
- Indications of TCEMEPs are particularly useful in surgeries involving.
Types of spinal cord pathology Ex- -spinal cord tumor.
- Intramedullary /extramedullary resections.
- Tethered cord syndrome
- deformity corrections- Example scoliosis /kyphosis .
- decompression surgeries.
- Metastasis Vertebrectomy. Etcetera.{ETC}.
- Peripheral nerve surgeries that may also impact motor function.
Cranium surgeries. Direct cortical and subcortical motor mapping / TCEMEPs.
Especially those near areas responsible for motor function example.
- Low – high grade gliomas or other form of tumors in or around the motor strip {cortex}
- Deeply seated tumors.
- Caudate nucleus
- Insular Glioma ETC.
- Motor potentials in Brainstem surgery.
Cervico-medullary junction Hemangioblastomas or other type of lesion also ,wherever the risk of direct or indirect injury of corticospinal tract.
Why monitor TCEMEPs.
- while drop signals in TceMEP amplitude/changes in phase or the absence of MEPs can indicate motor pathway compromise, which means need for intervention during ongoing procedure.
SSEPs {Somatosensory Evoked Potentials}.
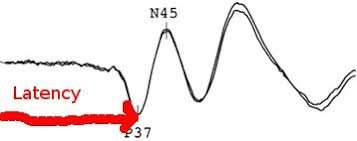
Principle– somatosensory evoked potentials {SSEPs} monitors the sensory pathways, specifically the dorsal columns of the spinal cord and the post central Gyrus { sensory cortex}.
Indications of modality- SSEPs are often used in procedures where the posterior cord/sensory pathways are at risk.
Spinal procedure especially those affecting the posterior spinal cord function/sensory nerve such as in.
- Intramedullary /extramedullary resections.
- Tethered cord syndrome
- deformity corrections- Example scoliosis /kyphosis .
- decompression surgeries
- Metastasis Vertebrectomy.
- laminectomies {ETC}.
SSEPs/EEG Plays important role in Cerebrovascular surgeries .
- MCA aneurysm clipping,
- ACA aneurysm clipping,
- ACOM aneurysm clipping,
- carotid endarterectomy/ Bypass Internal carotid to middle cerebral artery .
Purpose to monitor SSEP/EEG .
To monitor cortical integrity /Cerebral blood flow/collateral supply.
Cervico-medullary junction Hemangioblastomas or other type of lesion also ,wherever the risk of direct or indirect injury of posterior cord.
- Cranium surgeries that may involve areas of the post central gyrus{sensory cortex}.
- Why monitor SSEPs:
- The amount of reduction-50-80 % amplitude or absence of SSEP signals can indicate damage to the sensory pathways, which may precede permanent sensory deficits.
Which to Monitor? TCEMEPs Or SSEPs?
simultaneously TCEMEPs and SSEPs are frequently monitored together in high-risk surgeries involving the spinal cord, brain, brainstem or nerves, as they provide complementary real time information about both motor and sensory pathways.{Ascending and Descending tract}.
In exceptional cases, MEPs might be prioritized EX-in spine surgery where motor function is paramount concern, or SSEPs might be the focus EX in surgeries that primarily affect sensory function, or when motor function is less likely to be compromised, here will be primary priority to preserve motor function- to maintained to our daily life ,example while we walking ,buttoning of shirt ,eating food writing or typing, etcetera.
- Specific procedural context: The choice on whether to monitor MEPs or SSEPs, or both depends on:
- The location of the surgery.
- The risk factor to motor and sensory pathways.
- The surgeon’s moto (e.g., preventing motor deficits vs. sensory loss).Here my concern is to primary preserve motor function for our routine life but also sensory is important to feel the objects .

If the surgery involves both motor and sensory pathways {like spinal surgeries ,cranium surgeries or brainstem surgeries, {near the motor or sensory cortices}, both MEPs and SSEPs are typically monitored. However, if you have to choose one based on the specific risks to motor or sensory function, the monitoring technique should be tailored to the procedure.
Related to this article. TCEMEPs Or SSEPs?
https://neurointraoperative.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=2646&action=edit
