12.3 Before surgery IONM.
- patient’s medical history should be evaluated Preoperatively, including any previous neurological conditions.
- consent for IONM.
- Ensure proper positioning of the patient for surgery, like CP Angle , insular Glioma etc, considering IONM monitoring requirements .
- Set up IONM equipment and ensure it’s functioning properly.
12.4 IONM Baseline Recording:
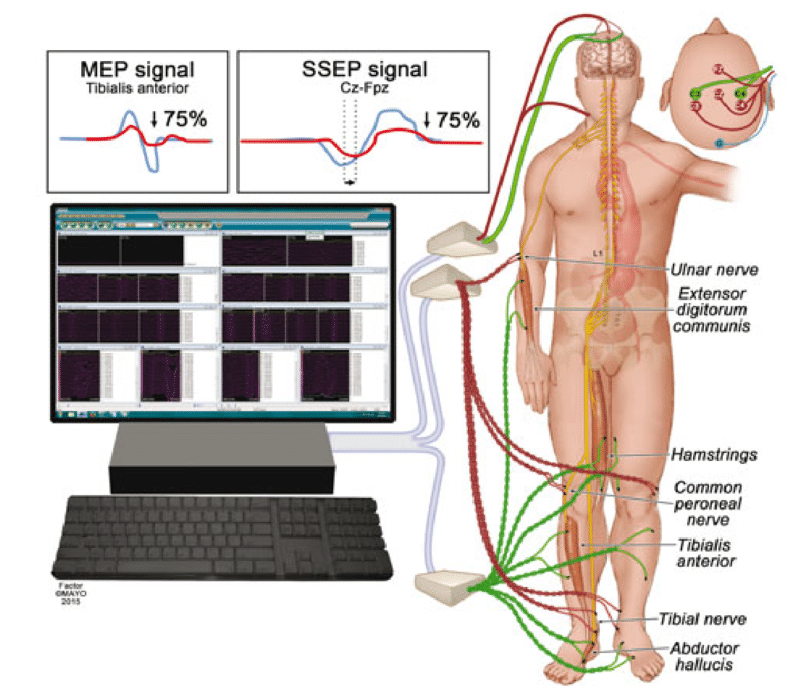
- Acquire baseline recordings of relevant neurophysiological parameters before the start of surgery. This may include somatosensory evoked potentials {SSEPs}, motor evoked potentials {MEPs}, Direct wave {D-wave} , mapping both cranium and spine, electromyography {EMG}, and others modality depending on the case.
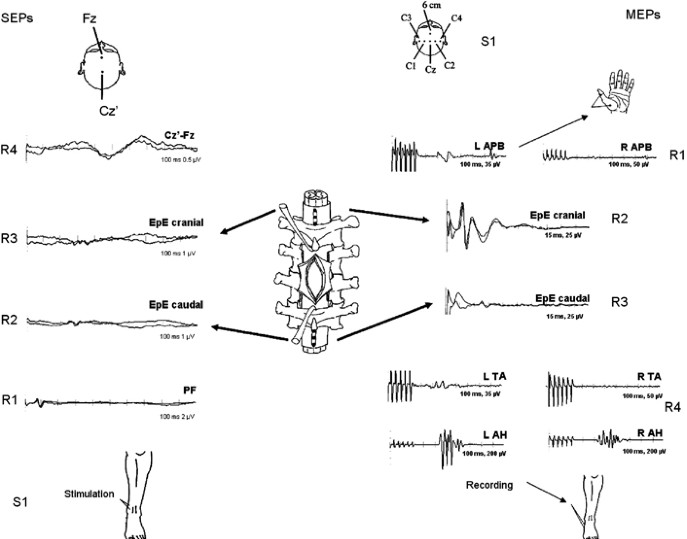
12.5 During Case .
- Continuously monitor neurophysiological signals throughout the procedure.
- Communication should be effective with the surgical team to coordinate actions based on monitoring findings.
- Reply immediately to any changes in neurophysiological signals.
- Ensure proper signal quality throughout the procedure.
- Document any surgical related changes, or abnormalities observed during procedure.

12.6 Stimulus and Recording Setup:
- Be sure proper placement of electrodes for stimulation and recording.
- Verify the integrity of stimulating electrodes and recording sensors.
- Set a appropriate stimulation threshold and parameter based on the specific procedure and patient pathology.
- Ensure recording system is properly calibrated and set up to acquire the signals.
12.7 Eliminate problems and Resolution:
- A plan in place for malfunction common issues with neuro-monitoring equipment.
- Communication should be effective with the surgical team about any challenges encountered during monitoring.
12.8 Postoperative Documentation:
- Document the intraoperative monitoring findings, including any changes observed during surgery.
- Communicate relevant findings to the surgical team .
- Assure proper documentation of the monitoring procedure in the patient’s medical records.

Follow-up and Review:
- Review monitoring data postoperatively to assess the integrity of neural structures and the effectiveness of the surgical intervention.
- Follow up with the patient as needed to monitor neurological function and recovery.

Conclusion.
Directory should be adapted and expanded based on the specific requirements of the surgical procedure and the preferences of the surgical team. It’s important to maintain clear communication and collaboration between the intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring team, the surgical team and Anesthesiology throughout the procedure.
{I hope these type of article will be useful for you.}
Related this article.
https://neurointraoperative.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=134&action=edit
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563203
Question.
- Why we should know about this subject?
- Which kind of surgery this subject is useful?.
- Correlation between IONM and extra-operative electrophysiology?.
- What exactly does IONM in neuro-spine surgery?.
- IONM is based on virtual reality.

1 thought on “Why You should know about intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring {IONM}?.”