
Introduction about Speech Mapping/Language.
- The aim of language mapping is to avoid language related deficits in language-processing functions post surgery.
- Pathology/Lesion resections adjacent to the dominant Sylvian fissure at the level of the superior temporal gyrus and in particular its posterior part and at the level of inferior frontal gyrus, are very much important indications for functional language mapping.
What exactly does Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring in these type of awake surgery.?.
- The electrical stimulation of eloquent language cortex causes an interruption of language functions. Thus during short epochs of stimulation different aspects of the language functions to be tested.
Why it is important pre-operative patients selections.
- Subject selections are essential, reason is many patients are not suited for such awake language mapping procedure because of age, anxiety, immaturity, inattention, or confusion.
- Also other hand possibilities are seizure type, lesion presence, handedness, or psychiatric history.
- Lower IQs are more often unable to cooperate effectively during language mapping in awake craniotomies.
- Lesions near the primary speech centers should be carefully screened prior to surgery with neuropsychiatric testing and fMRI.
During electrical stimulation what can happen in awake surgery?
- While electrical cortical/subcortical stimulation may lower the threshold for epileptiform activity which means the possibility of triggering a seizure. {Ice cold irrigation should be there in surgeon hand for irrigate the stimulated areas to minimize the the seizure activity}.
- In addition to interfering with accurate identification of the eloquent cortex, triggered GTCZ poses additional risks in awake patients that are related to possible compromise of airway control.
what are the points for Technical Aspects.
- For language mapping we usually use the bipolar long space Penfield or ozomen stimulation probe.
- In a general term, in order to produce disruption of language function the electrical impulse need to repeat, with a relatively high frequency and in a continuous fashion, during the epoch of stimulation.
- Here big role of handheld bipolar stimulator probe to map cortical and subcortical speech eloquent cortex.
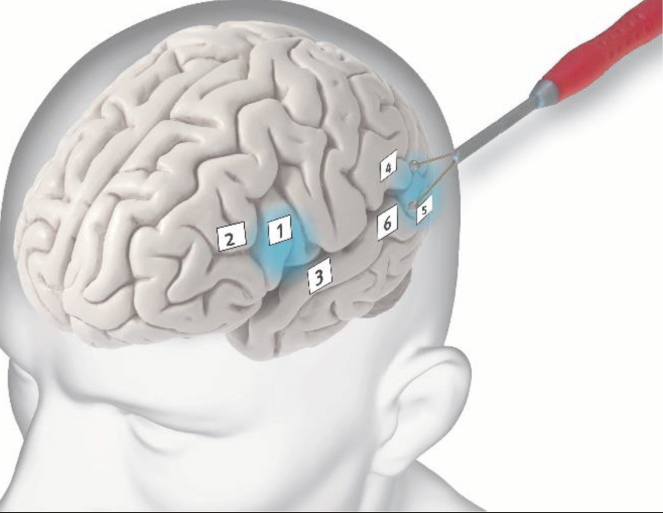
- Continuous neurophysiological monitoring allows assessment of the language function, which is not possible under general anesthesia.
How to test patient’s related results and interpretation.
Using function related specific tasks.
Perioperative to procedure baseline verbal function must be established for,
- Verbal fluency repetition.
- Visual object naming.
- Sentence comprehension and word generation.
- Patients preoperative should be trained to perform the same types of tasks that will used during the procedure.
Verbal fluency and repetition.
These tasks should be tested in particular if the lesion to be resected is in close proximity to the inferior frontal region, corresponding to the Broca’s area or the arcuate fasciculus.
To check verbal fluency can be performed by tasks such,
- counting numbers like 1-10 .{positive area -speech arrest while counting the numbers}.
- counting by 2, repetition of sentences, or engaging patients in conversations about their hobbies, family, etc.
- Also like enumeration of the months of the year, days of the week, forward and
backward.
Comprehensive sentence to the subject for identify aphasias.
- Perioperative surgery Showing some sort of picture like Banana, Apple, Fan etc.{During stimulation, positive area– confusion while showing the pictures or not able to recognize those picture which had been shown preoperative.}.
- Established by showing patients two sentences that appear to be similar but contain a single word that has been substituted for another with a different or similar meaning.
- This kind of perioperative task usually activates perisylvian cortices, which participate in semantic processing and should be carefully tested in particular for resections involving the posterior part of the superior temporal gyrus.
Anomia and dysfunction of the verbal fluency .
- This is triggered by stimulation of the arcuate fasciculus and insular connections.
- To activate this fibers, can be used Combination of Repetition, word generation. { positive area -Difficulty in naming the word while showing, during the procedure.}
- While stimulation being done a 4-6 contact grid electrode will be preferred at stimulation site, to see the electrographic seizure .

Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring IONM speech mapping cortical and subcortical is feasible technique for awake lesion resection surgery, while resecting the tumor near to the functional language area.
Related to this article.
https://neurointraoperative.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=1687&action=edit
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8191642
Question.
Q-Why ice cold water is mandatory for awake speech mapping?.
A-Yes its a mandatory because cold saline is useful to stop stimulation related seizure.
Q-How helps long space bipolar probe to map?.
A- Long space bipolar probe covers little long area of gyrus.
Q-Why we prefer only conscious awake craniotomy?.
A- Because patient should follow the command during procedure.
Q-What we should do if seizure develops during stimulation?.
A-Primary irrigation with ice cold saline , if does not get control secondary bolus of propofol because this drug does not hamper the signals of subcortical fibers rather than midaz group of drugs.

2 thoughts on “Functional Mapping in Eloquent cortex, speech mapping.”