The Blink Reflex.

- In perioperative Blink Reflex usually assess the function of brainstem during posterior fossa /skull base surgery, and its valuable neurophysiological monitoring technique. This modality helps the neurosurgeon to see the integrity along with continuity of brainstem and its associated pathways particularly pons division of brainstem { Cranial nerves trigeminal and facial}
Essential.
- Real time Nerve Continuity Monitoring. In Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring {IONM}The blink reflex modality evaluates the functional status of the trigeminal nerve (Vth ) and the facial nerve (VIIth ), which are crucial for motor and sensory functions in the face.
- Early Detection from the Iatrogenic Injury. Signal changes in Blink Reflex study may provide immediate feedback about nerve potential damage, allowing for prompt intervention.
- Guidance for Resection of pathology. During the procedure involving tumors or any vascular lesion in or around brainstem, the modality Blink Reflex can guide the surgeon in real time to avoid important /critical areas.
Mechanism.
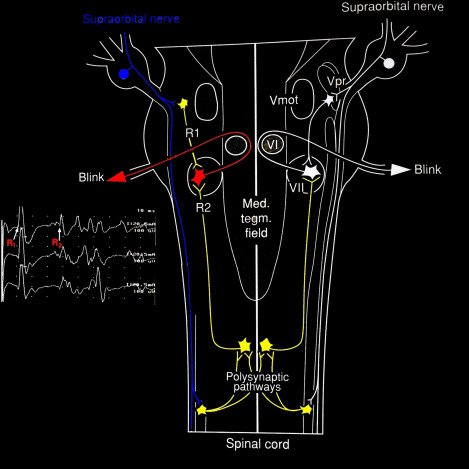
- The intraoperative modality blink reflex involves a sensory stimulus { supraorbital area, usually through the cornea} and a motor response {blinking}, mediated by the brainstem circuits. {afferent fifth and efferent from the seventh cranial nerves}.
- Stimulus supraorbital nerve to the cornea activates the sensory fibers{afferent} of the trigeminal nerve, sending signals to the pons brainstem, which then triggers motor output{efferent} through the facial nerve.
Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring Technique {Blink Reflex}.
- For Stimulation– A electrical stimulus such as a subdermal twisted needle 2-3 centimeter electrode over supraorbital part at 45 degree parallel to the skin, to the cornea can elicit the blink reflex.
- Parameters- Start with at least 2-3 pulses @2-3 Hz ,pulse duration 300-500 micro second ,intensity of stimulus as per threshold. { Multiple pulses are required because this reflex study being recorded in General Anesthesia as we know anesthesia drugs blocks synapses and its polysynaptic reflex study.
- Neuro-Electrophysiological Monitoring– Perioperative electromyography {PEMG} usually used to assess the blink response. Electrodes are placed on the orbicularis oculi muscle to record muscle activity.
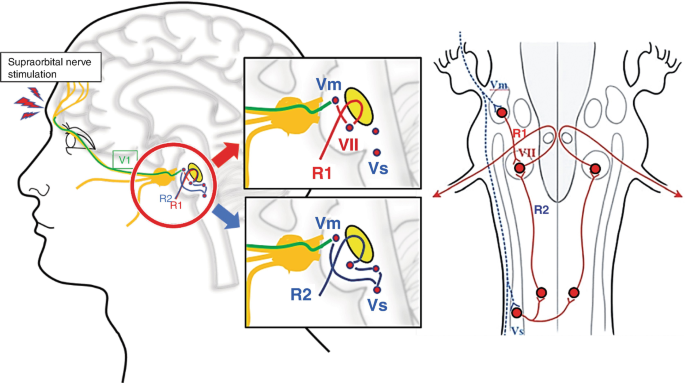
Real time Clinical Implications.
- Interpretation of Electromyography{EMG} Responses- Early sign, delayed latencies or secondary diminished reflex or an absent during procedure may indicate potential damage or compression of the involved nerves, or indirect /direct compression on pons{Brainstem} so that necessitating careful reconsideration of surgical approach.
- Post surgery Outcomes- Intact/Preservation of the blink reflex correlates with better functional outcomes and reduced complications related to facial sensation and movement.

As per literature and my experience suggest that Blink Reflex is a sensitive and more valuable intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring method that can be used in addition to facial nerve motor evoked potential corticobulbar tract CoMEPs /TEMG during posterior fossa or skull base surgeries to assess real-time facial nerve integrity and predict prognosis.
Related to this article .
https://neurointraoperative.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=1590&action=edit
