Introduction about Corticobulbar MEP
The muscles of the face, head and neck are controlled by the corticobulbar system, which terminates on motor neurons within brain-stem motor nuclei. Contrast this to the corticospinal tract were the cerebral cortex connects to spinal motor neurons, and controls movement of the torso, upper and lower limbs..
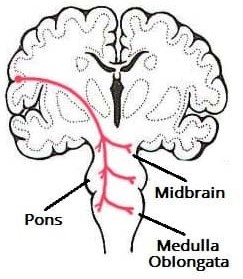
Which cranial nerve comes from this tracts. To record Corticobulbar MEP.
The corticobulbar tract is a two-neuron path which unites the cerebral cortex with the cranial nerve nuclei in the brainstem involved in motor functions (apart from the oculomotor nerve).
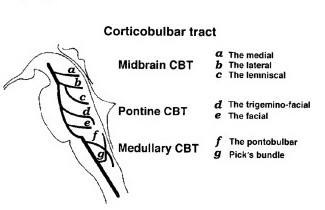
How helps Corticobulbar MEP. CBT TCEMEP In skull base and posterior fossa surgery. {Especially tumor is giant in size and envelops the facial nerve}.
History.
An Facial Nerve MEP elicited by transcranial electrical stimulation was first reported by Merton and Morton in 1980, and the FNMEP was applied in tumorectomy by Zhou et al in 2001.
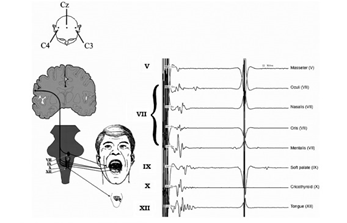
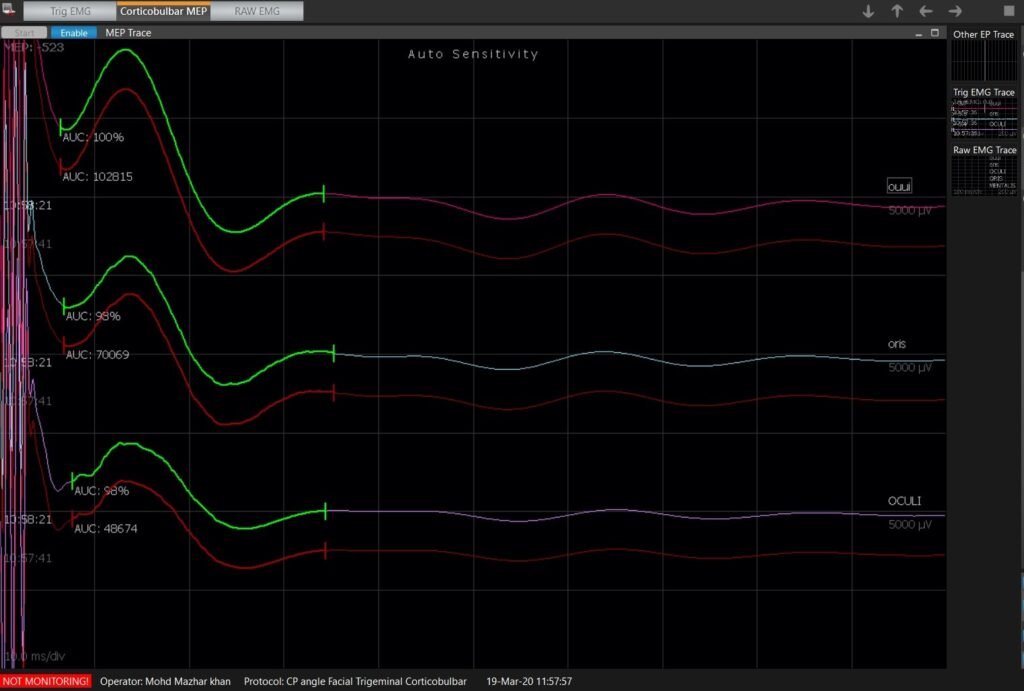
- This monitoring approach records the CMAP in the target muscle (orbicularis oculi,orbicularis oris and mentalis) evoked by stimulating the facial nerve motor cortex. Transcranial electrical stimulation is less invasive than conventional direct electrical stimulation, and the FNMEP is considered to be closely associated with the postoperative facial nerve function.
- In CPA tumorectomy, transcranial FNMEP can be applied for real-time evaluation of the facial nerve function, facilitating the early identification of facial nerve damage and promoting maximal safe resection of the CPA tumors with facial nerve preservation.
- The FNMEP has significant superiority when the tumor is giant in size and envelops the facial nerve. The alarm criteria of FNMEP have yet to be established. Some scholars recommend a 50% reduction in amplitude as an indicator for predicting facial nerve damage
- Bulbar MEP helps to see the function of cranial nerves and its continuity , anatomical preservation throughout the procedure which Trigger electromyography only assess the peripheral function.
Free Run Electromyography. Corticobulbar MEP .
- Free run electromyography also helps to see the abnormal activity { Real time } while surgeon working close the facial nerve .
- If activity shows high frequency bursts of motor unit potential and the sound similar to end plate spikes , Neurotonic discharge or myotonia would be possibility of indirect injury of nerve like, pulling affect during tumorectomy . Iatrogenic injury , cautery , instruments ,etc.
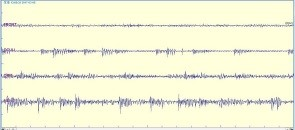
- Free running electomyography showing abrupt increase in activity in left frontalis, orbicularis oculi, orbicularis oris and mentalis muscles. This above image , free running EMG showed an abrupt increase in activity, The high frequency bursts of motor unit potential and the sound was sustained for approximately 2 minutes and disappeared suddenly.
Stimulation parameter, Corticobulbar MEP .
- For stimulation corkscrew electrode , C3-C4 or C4-C3 Montage can be preferred as per 10-20 EEG electrode placement to record muscle action potential from the target muscles to interpreted the signals.
- Number of pulses set at 2-3 , pulse width 75 microsecond and Inter stimulation interval {ISI} 2-3 millisecond , Train of stimuli @ 1 Hz, start with least current after wear off muscle relaxant effect, like 90-110 Volt to avoid volume conduction and other motor pathway activity ,{ false negative result}.
Recordings Corticobulbar MEP.
The stimulation of the CBT is can be done using Transcranial Electrical Stimulation (TES) consisting of short high-frequency train of stimuli. Since TES is can applied at the scalp over the Face ,Neck motor area that represents the muscles innervate by Cranial Motor Nucleus .
Conclusion. Corticobulbar MEP .
Cerebro Pontine Angle {CPA} tumorectomy is a challenging and delicate surgical procedure due to the complicated local anatomical structures. The FNMEP can elicited by transcranial electrical stimulation, is an effective and safe approach for predicting the short-term and long-term facial nerve function following CPA tumorectomy. A drop of amplitude ,compound muscle action potential {CMAP} in FNMEP is a indicator for the prediction of postoperative facial nerve damage.
Question /Answer. Corticobulbar MEP .
- Choice of Anesthesia Drugs?
- TIVA would be preferred to record quality of signals because these drugs does not act on Neuromuscular Junction{NMJ}
- Number of pulses 2-3 or 5 are enough to record CBT,MEP?.
- Corticobulbar tract is very short compare corticospinal tract , above number of pulses is enough to record signals .
- Why Inter stimulation interval are important especially in these parameter ?.
- If we keep ISI 3-4 millisecond this will overlap with the real muscle potential means { stimulation artifact will mix with signals } , And as per absolute refectory of neuron we can not go less than 1-2 millisecond because cell needs time to re-depolarized to produce another action potential.
- This type of article may be helpful for you . please do comment and share.
Related to this article.
https://neurointraoperative.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=1693&action=edit

1 thought on “Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring (IONM) Role in Corticobulbar MEP Transcranial Electrical Motor Evoked potential in skull base and posterior fossa surgery .”